Tuesday, 28 February 2012
Wednesday, 22 February 2012
7.9

background radiation.pptx Download this file
7.9
12 January 2012 10:24· 7.9 recall the sources of background radiation
> Whys Guy
· http://youtu.be/CUqdLwIITWM
7.4 and 7.5
7.4 and 7.5 starter 01 February 2012 10:00 Tell the person next to you…
· What are the 7 parts of the electromagnetic spectrum you learnt in P3, Waves?
· What are they in order of increasing frequency? > (Note that microwaves are missing from this animation!) Answers
· Radio waves
· Microwaves
3. Infra Red
4. Visible
5. Ultra violet
6. X-Rays
7. Gamma Rays 7.4 and 7.5 12 January 2012 10:24
· 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process
· 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power Producing Alpha, Beta and Gamma radiation
· http://youtu.be/pHUgL_RS9ng
> >
Penetrating Power
· http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=48JQaZHuFsQ&feature=youtu.be
· http://youtu.be/61y2GTr0MlQ
> >
> >
Ionisation
> > > Effect of magnetic and electric fields
>
> 











· What are the 7 parts of the electromagnetic spectrum you learnt in P3, Waves?
· What are they in order of increasing frequency? > (Note that microwaves are missing from this animation!) Answers
· Radio waves
· Microwaves
3. Infra Red
4. Visible
5. Ultra violet
6. X-Rays
7. Gamma Rays 7.4 and 7.5 12 January 2012 10:24
· 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process
· 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power Producing Alpha, Beta and Gamma radiation
· http://youtu.be/pHUgL_RS9ng
> >
Penetrating Power
· http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=48JQaZHuFsQ&feature=youtu.be
· http://youtu.be/61y2GTr0MlQ
> >
> >
Ionisation
> > > Effect of magnetic and electric fields
>
>

producing a,b,g.pptx Download this file

penetrating power.swf Download this file

ionisation.pptx Download this file

Interactive simulation - penetration of radiation.swf Download this file

effect of magnetic field on a,b,g.swf Download this file

effect of electric field on a,b,g.swf Download this file

e-m spec.swf Download this file

DJFPh109ioniz2.swf Download this file

DJFPh109gammy5.swf Download this file

DJFPh107pene3.swf Download this file

decays emitting a,b,g.swf Download this file

Animation - ionisation of atom by radiation.swf Download this file
7.8

detection of radiation.pptx Download this file
7.8
12 January 2012 10:24· 7.8 understand that ionising radiations can be detected using a photographic film or a Geiger-Muller detector
>
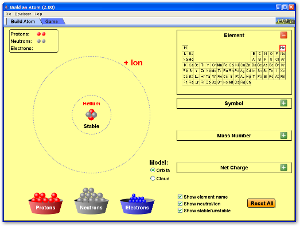
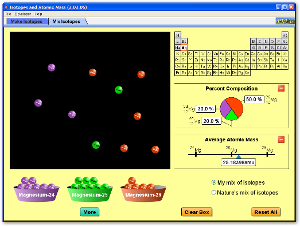
7.3

Isotopes.ppt Download this file
7.3
12 January 2012 10:24· 7.3 understand the terms atomic (proton) number, mass (nucleon) number and isotope
> PhET animation - build an atom 31 January 2012 13:34
> Website http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build-an-atom Embed code for your blog PhET animation - isotopes 31 January 2012 13:34
> Website http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/isotopes-and-atomic-mass Embed code for your blog
7.2
7.2 starter 31 January 2012 11:35 Tell the person next to you…
· The names of 3 subatomic particles
· What properties do they have?
>
> 7.2 11 January 2012 14:49
· 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as 146C to describe particular nuclei
>
> 



· The names of 3 subatomic particles
· What properties do they have?
>
> 7.2 11 January 2012 14:49
· 7.2 describe the structure of an atom in terms of protons, neutrons and electrons and use symbols such as 146C to describe particular nuclei
>
>

sub-atomic particles - drag and drop.swf Download this file

Proton number and mass number.ppt Download this file

atomic structure of Li - mass and proton numbers.swf Download this file

atomic structure - electrons orbiting the nucleus.swf Download this file
P7 Keywords - First Homework

P7 keywords and mixed definitions.doc Download this file
Homework for next Wednesday
P7 Keywords - First Homework 02 September 2010 18:41 Step 1 = Unscramble the Keywords and Mixed Definitions sheet. 4 options:· Kinaesthetic Learners = Cut and Stick into your exercise book. Take a photo of your work and send to your blog
· Kinaesthetic Learners = Cut and Paste in the Word document and send to your blog
· Visual Learners = Copy out into your exercise book. Take a photo of your work and send to your blog
· Visual Learners = Type out and send to your blog Step 2 = Check your keywords by using one of the following online games. Make corrections to your work in a different coloured pen/font so that you can see your mistakes clearly.
· http://www.patana.ac.th/LearningObjects/%7BFC7DE36D-42FC-47FC-B072-2E4EA5DFDB...
· http://www.patana.ac.th/LearningObjects/%7BD0CC1663-8A7B-4215-B618-A645F8A399...
· http://www.patana.ac.th/LearningObjects/%7BE40854B9-2D1A-4ECA-B286-6B70310AD2...
>
P7 student objectives sheet

P7 IGCSE Physics Student Objectives.doc Download this file
Kavin (Nik) Supatravanij
Bangkok Patana School, 11B
Sunday, 12 February 2012
6.19 and 6.20 Plenary answers
6.19 and 6.20 Plenary answers 01 December 2011 18:08
[cid:image001.png@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/2=80/20 Vs=8V
b. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/10=20/100 Vs=2V
c. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/240=20/400 Vs=12V
d. Vs/Vp=Ns/Np Vs/4=2000/50 Vs=160V [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
2. Vs/Vp=ns/np 3/24=ns/480 ns=60turns [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Iron (Why? Iron is a magnetically soft material - it can be magnetised and lose its magnetism easily. This is necessary in a transformer as the magnetic field needs to change repeatedly)
b. electrical energy in the primary coil => magnetic energy in the core =>electrical energy in the secondary coil
c. dc current produces a steady magnetic field in the core. To induce a current in the secondary coils there must be a changing magnetic field in the core. [cid:image004.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Step down (because the voltage decreases)
b. Vs/Vp=ns/np 12/240=ns/1000 ns=50turns
c. P = V x I 24 = 12 x I I = 2A
d. Power in secondary = 24W
e. Power in primary = 24W
f. P = V x I 24 = 240 x I I = 0.1A
g. The current would be greater/double Why? Efficiency = Useful Pout/Total Pinx100 50 = 24/Total Pin x 100 Total Pin = 48W P = V x I 48 = 240 x I I = 0.2A
[cid:image001.png@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/2=80/20 Vs=8V
b. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/10=20/100 Vs=2V
c. Vs/Vp=ns/np Vs/240=20/400 Vs=12V
d. Vs/Vp=Ns/Np Vs/4=2000/50 Vs=160V [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
2. Vs/Vp=ns/np 3/24=ns/480 ns=60turns [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Iron (Why? Iron is a magnetically soft material - it can be magnetised and lose its magnetism easily. This is necessary in a transformer as the magnetic field needs to change repeatedly)
b. electrical energy in the primary coil => magnetic energy in the core =>electrical energy in the secondary coil
c. dc current produces a steady magnetic field in the core. To induce a current in the secondary coils there must be a changing magnetic field in the core. [cid:image004.jpg@01CCE7CB.95BA8CB0]
a. Step down (because the voltage decreases)
b. Vs/Vp=ns/np 12/240=ns/1000 ns=50turns
c. P = V x I 24 = 12 x I I = 2A
d. Power in secondary = 24W
e. Power in primary = 24W
f. P = V x I 24 = 240 x I I = 0.1A
g. The current would be greater/double Why? Efficiency = Useful Pout/Total Pinx100 50 = 24/Total Pin x 100 Total Pin = 48W P = V x I 48 = 240 x I I = 0.2A
Plenary questions
6.18 Plenary Multichoice questions 01 December 2011 18:13 > 6d Plenary answers
[cid:image001.png@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
[cid:image002.png@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
[cid:image003.jpg@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
a.deflection to the left
b. deflection to the left
c. no deflection
1. push the magnet in quicker
2. use a coil with more turns
3. use a stronger magnet P6 Plenary: 10 multi-choice questions 14 December 2011 12:49 > 

[cid:image001.png@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
[cid:image002.png@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
[cid:image003.jpg@01CCE7CD.E0122820]
a.deflection to the left
b. deflection to the left
c. no deflection
1. push the magnet in quicker
2. use a coil with more turns
3. use a stronger magnet P6 Plenary: 10 multi-choice questions 14 December 2011 12:49 >

P6 Multichoice questions.pptx Download this file

6d Plenary Multichoice questions.pptx Download this file
Friday, 3 February 2012
6.17
6.17 01 December 2011 18:08
· 6.17 recall the structure of a transformer, and understand that a transformer changes the size of an alternating voltage by having different numbers of turns on the input and output sides 6.17 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
· If you…
· Turn the powerpack to dc [cid:image001.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] No current is induced in the Secondary Coil. To induce current you need a changing magnetic field and this is not produced by applying dc to the Primary Coil
· Turn the powerpack to ac [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] ac is induced in the Secondary Coil. To induce current you need a changing magnetic field and this is produced by applying ac to the Primary Coil
3. Increase the number of turns in the Secondary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils increases
4. Increase the voltage on the Primary Coil [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils increases
5. Decrease the number of turns in the Secondary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils decreases
6. Decrease the voltage on the Primary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils decreases
· 6.17 recall the structure of a transformer, and understand that a transformer changes the size of an alternating voltage by having different numbers of turns on the input and output sides 6.17 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
· If you…
· Turn the powerpack to dc [cid:image001.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] No current is induced in the Secondary Coil. To induce current you need a changing magnetic field and this is not produced by applying dc to the Primary Coil
· Turn the powerpack to ac [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] ac is induced in the Secondary Coil. To induce current you need a changing magnetic field and this is produced by applying ac to the Primary Coil
3. Increase the number of turns in the Secondary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils increases
4. Increase the voltage on the Primary Coil [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE252.359BA450] The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils increases
5. Decrease the number of turns in the Secondary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils decreases
6. Decrease the voltage on the Primary Coil The size of the induced voltage in the secondary coils decreases
6.20
6.20 01 December 2011 18:08
· 6.20 recall and use the relationship (for 100% efficiency): input power = output power Vp Ip = Vs Is
> 6.19 and 6.20 Plenary 01 December 2011 18:08
>
[cid:image001.png@01CCE252.4D9BE600] 

· 6.20 recall and use the relationship (for 100% efficiency): input power = output power Vp Ip = Vs Is
> 6.19 and 6.20 Plenary 01 December 2011 18:08
>
[cid:image001.png@01CCE252.4D9BE600]

transformer worksheet.doc Download this file

transformer animation with sliders and example calculations.swf Download this file
6.19

transformer quick quiz.swf Download this file
6.19
01 December 2011 18:08· 6.19 recall and use the relationship between input (primary) and output (secondary) voltages and the turns ratio for a transformer: input (primary) voltage = primary turns output (secondary) voltage secondary turns Vp/Vs = np/ns
>
6.18

National grid worksheet.doc Download this file
6.18
01 December 2011 18:08· 6.18 explain the use of step-up and step-down transformers in the large-scale generation and transmission of electrical energy
· http://youtu.be/LZKhGGBcYFI
6.16
6.16 01 December 2011 18:08
· 6.16 describe the generation of electricity by the rotation of a magnet within a coil of wire and of a coil of wire within a magnetic field; also describe the factors which affect the size of the induced voltage
· Magnet rotating near coil [cid:image001.png@01CCE252.2901EF10]
· Coil rotating near magnet [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.2901EF10]
· ac generator > [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE252.2901EF10] 6.16 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
>
· Connect a hand turned generator to a light bulb. Observe the light bulb when you...
· Rotate the generator slowly The induced voltage decreases
· Rotate the generator quickly The induced voltage increases
3. Increase the strength of the magnet The induced voltage increases
4. Increase the number of turns in the coil The induced voltage increases 6.16 Plenary 17 January 2012 15:20
· What are the 3 ways that you can increase the size of the current induced in a generator? Answers
· Increase the strength of the magnets
· Increase the speed of the relative motion
· Use a coil with more turns of wire 
· 6.16 describe the generation of electricity by the rotation of a magnet within a coil of wire and of a coil of wire within a magnetic field; also describe the factors which affect the size of the induced voltage
· Magnet rotating near coil [cid:image001.png@01CCE252.2901EF10]
· Coil rotating near magnet [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.2901EF10]
· ac generator > [cid:image003.jpg@01CCE252.2901EF10] 6.16 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
>
· Connect a hand turned generator to a light bulb. Observe the light bulb when you...
· Rotate the generator slowly The induced voltage decreases
· Rotate the generator quickly The induced voltage increases
3. Increase the strength of the magnet The induced voltage increases
4. Increase the number of turns in the coil The induced voltage increases 6.16 Plenary 17 January 2012 15:20
· What are the 3 ways that you can increase the size of the current induced in a generator? Answers
· Increase the strength of the magnets
· Increase the speed of the relative motion
· Use a coil with more turns of wire

AC Generator animation.swf Download this file
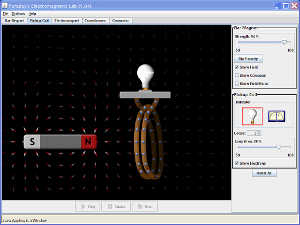
Faraday's Lab animation
Faraday's Lab animation 28 November 2011 15:06 > Website: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/faraday 6.16 generator simulation 28 November 2011 15:06 Website: http://www.walter-fendt.de/ph14e/generator_e.htm
6.15
6.15 starter 01 December 2011 18:08
· What’s the motor effect?
· "If there’s a magnetic field perpendicular to a current in a wire, the wire moves in a direction perpendicular to the field and the current" (FLHR)
· So what about if we move a wire in a magnetic field? What happens in the wire?
>
· When we move a wire in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire 6.15 01 December 2011 18:08
· 6.15 recall that a voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it; also recall the factors which affect the size of the induced voltage
[cid:image001.png@01CCE252.11AB81F0] [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.11AB81F0] >
> 6.15 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
· If you...
· Push the North pole of the magnet into the coil A negative current flow shown by a negative deflection on the ammeter
· Keep the magnet stationary within the coil No current
3. Pull the North pole of the magnet out of the coil A positive current
4. Push the South pole of the magnet into the coil A positive current
5. Push the North pole of the magnet slowly into the coil A smaller negative current
6. Push the North pole of the magnet quickly into the coil A larger negative current
7. Change the coil for one with more turns of wire and push the North pole of the magnet into the coil A larger negative current
8. Push the North pole of a neodymium (strong) magnet into the coil A larger negative current
9. Move the magnet in and out of the coil repeatedly. What sort of current is this? An alternating current 6.15 Plenary answers 16 January 2012
· Explain carefully how you can induce a current in a wire (3 marks)
· State 3 ways you can increase the size of this induced current (3 marks) Answers
· The wire must be perpendicular to a magnetic field
· The wire and magnetic field must move relative to each other – the wire must “cut” through the magnetic field lines/lines of magnetic flux as it moves
· A current is induced in the wire. The induced current is perpendicular to both the field and the motion
· Increase the strength of the magnets
· Increase the speed of the relative motion
· Use a coil of wire instead of a single piece of wire 


· What’s the motor effect?
· "If there’s a magnetic field perpendicular to a current in a wire, the wire moves in a direction perpendicular to the field and the current" (FLHR)
· So what about if we move a wire in a magnetic field? What happens in the wire?
>
· When we move a wire in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire 6.15 01 December 2011 18:08
· 6.15 recall that a voltage is induced in a conductor or a coil when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it; also recall the factors which affect the size of the induced voltage
[cid:image001.png@01CCE252.11AB81F0] [cid:image002.jpg@01CCE252.11AB81F0] >
> 6.15 Practical - model answers 17 January 2012 14:33
· If you...
· Push the North pole of the magnet into the coil A negative current flow shown by a negative deflection on the ammeter
· Keep the magnet stationary within the coil No current
3. Pull the North pole of the magnet out of the coil A positive current
4. Push the South pole of the magnet into the coil A positive current
5. Push the North pole of the magnet slowly into the coil A smaller negative current
6. Push the North pole of the magnet quickly into the coil A larger negative current
7. Change the coil for one with more turns of wire and push the North pole of the magnet into the coil A larger negative current
8. Push the North pole of a neodymium (strong) magnet into the coil A larger negative current
9. Move the magnet in and out of the coil repeatedly. What sort of current is this? An alternating current 6.15 Plenary answers 16 January 2012
· Explain carefully how you can induce a current in a wire (3 marks)
· State 3 ways you can increase the size of this induced current (3 marks) Answers
· The wire must be perpendicular to a magnetic field
· The wire and magnetic field must move relative to each other – the wire must “cut” through the magnetic field lines/lines of magnetic flux as it moves
· A current is induced in the wire. The induced current is perpendicular to both the field and the motion
· Increase the strength of the magnets
· Increase the speed of the relative motion
· Use a coil of wire instead of a single piece of wire

induction - magnet moving into coil (slow, fast, poles reversed).swf Download this file

current induced in a moving wire_2.swf Download this file

current induced in a moving wire.swf Download this file
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)